Acute barbiturate poisoning is a medical emergency that requires prompt intervention. Barbiturates, once popular for treating anxiety and insomnia, have now been largely replaced by safer alternatives. However, these drugs are still found in various forms and can lead to severe poisoning if misused. Understanding how acute barbiturate poisoning affects the body, its symptoms, and its treatment options is crucial for medical professionals, students, and the general public.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of acute barbiturate poisoning.
What is Acute Barbiturate Poisoning?
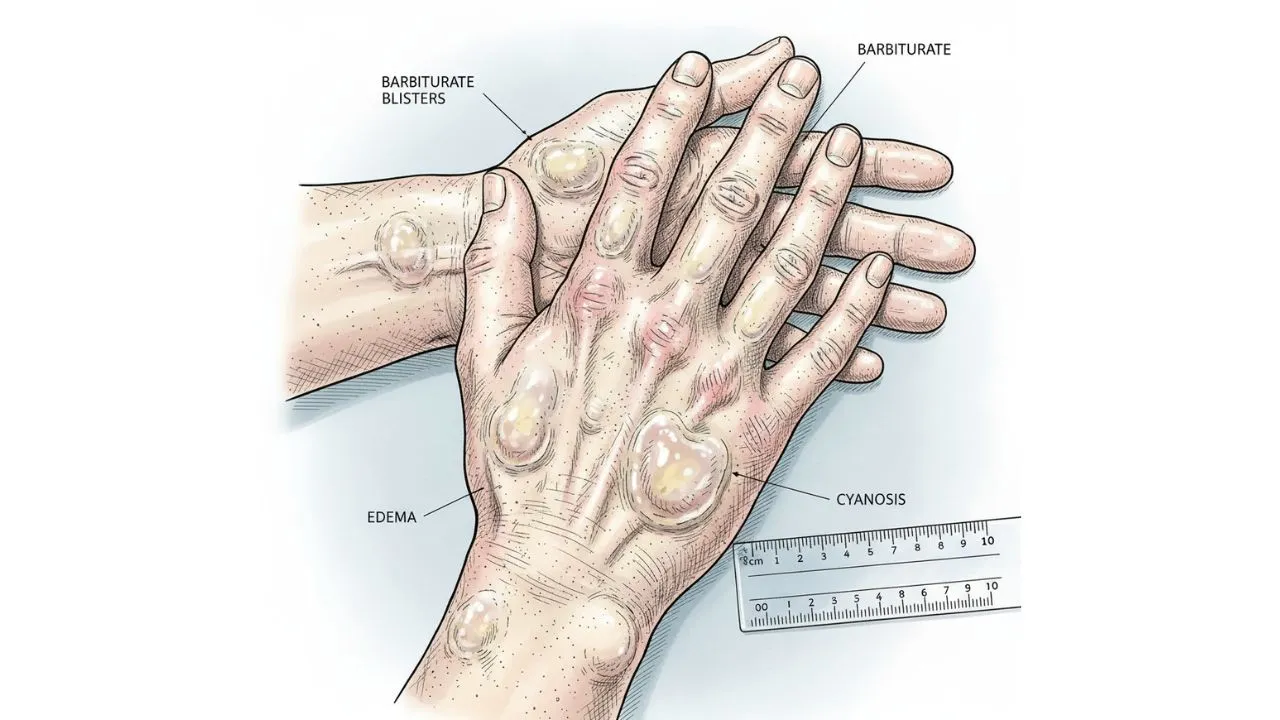
Acute barbiturate poisoning refers to the harmful effects caused by an overdose of barbiturates. Barbiturates are central nervous system depressants that were once commonly prescribed for conditions like anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. When consumed in excessive amounts, barbiturates can cause serious toxicity and potentially life-threatening symptoms.
Barbiturates work by enhancing the activity of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), an inhibitory neurotransmitter, leading to sedation, muscle relaxation, and a slowing down of brain activity. In high doses, they can cause respiratory depression, coma, and even death.
For more information on toxicology in medical practice, visit our Medical Poisoning Guide.
Why It Matters: The Importance of Recognizing Acute Barbiturate Poisoning
Understanding about this poisoning is vital for several reasons:
- Public Health Concern: While the use of barbiturates has declined, they are still present in medical settings, and their misuse continues to pose a risk, particularly in cases of overdose or intentional ingestion.
- Medical Relevance for MBBS Students: Medical students need to familiarize themselves with the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment protocols associated with barbiturate poisoning as part of their clinical education.
- Real-Life Application: For healthcare providers, timely intervention can save lives. Knowing the symptoms and treatment options can help them deliver appropriate care to patients in distress.
Key Points to Understand Acute Barbiturate Poisoning
- Primary cause: Overdose of barbiturates or accidental ingestion.
- Symptoms: Respiratory depression, coma, hypotension, and confusion.
- Management: Immediate hospitalization, administration of activated charcoal, and supportive treatment.
- Prognosis: Timely intervention can lead to a good recovery, but severe cases may result in death.
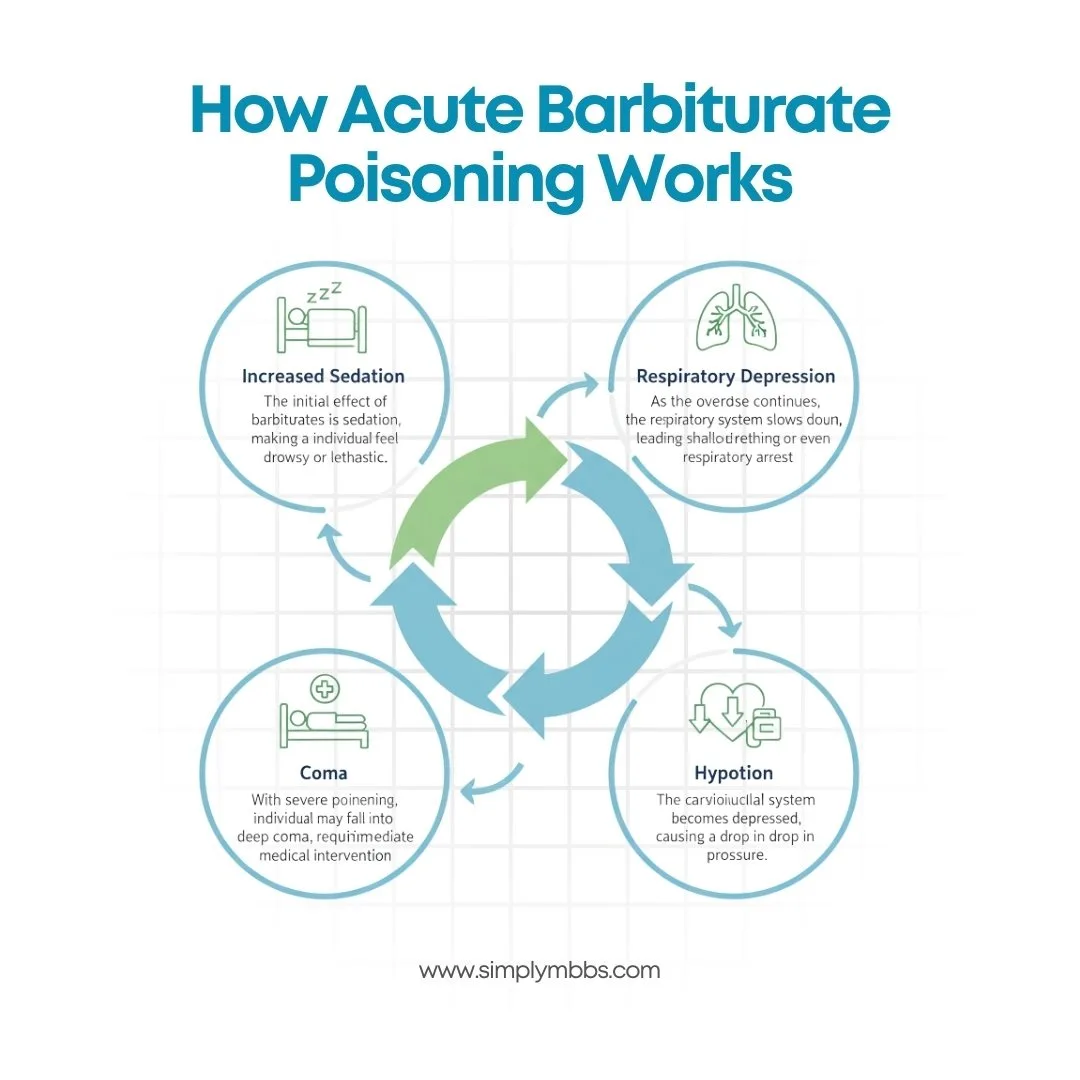
How Acute Barbiturate Poisoning Works
The pathophysiology of this poisoning involves the inhibition of the central nervous system (CNS). Barbiturates bind to the GABA-A receptor, enhancing the effects of GABA, which in turn suppresses neuronal excitability. This leads to a sedative effect, but when the dose exceeds the therapeutic range, it can cause significant CNS depression.
Here’s how the body responds to an overdose:
- Increased Sedation: The initial effect of barbiturates is sedation, making the individual feel drowsy or lethargic.
- Respiratory Depression: As the overdose continues, the respiratory system slows down, leading to shallow breathing or even respiratory arrest.
- Hypotension: The cardiovascular system becomes depressed, causing a drop in blood pressure.
- Coma: With severe poisoning, the individual may fall into a deep coma, requiring immediate medical intervention.
Comparison: Barbiturate Poisoning vs Other Types of Poisoning
It’s important to understand how the poisoning compares with other types of poisoning, such as opioid or benzodiazepine poisoning. Here’s a brief comparison:
| Feature | Barbiturate Poisoning | Opioid Poisoning | Benzodiazepine Poisoning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | CNS depression, GABA enhancement | CNS depression, mu-opioid receptor binding | CNS depression, GABA enhancement |
| Symptoms | Respiratory depression, coma, hypotension | Respiratory depression, pinpoint pupils, bradycardia | Sedation, confusion, dizziness |
| Treatment | Activated charcoal, supportive care | Naloxone, supportive care | Flumazenil (rarely used), supportive care |
| Prognosis | Depends on the dose and timing of treatment | High recovery rate with timely intervention | Good prognosis with proper care |
While both barbiturate and opioid poisoning can lead to life-threatening symptoms like respiratory depression, their treatments differ significantly. Barbiturates require prompt supportive care, while opioids can often be reversed with naloxone.
Expert Insights / Data-Driven Points
- According to a study published in The American Journal of Emergency Medicine, barbiturate overdoses contribute to a significant number of poisoning cases in emergency rooms, with a mortality rate of 5-10% in untreated severe cases.
- The U.S. Poison Control Centers report an increase in barbiturate poisoning, particularly among older adults who may have been prescribed these drugs in the past and are unaware of the dangers of overdose.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Acute Barbiturate Poisoning Management
- Delayed Diagnosis: It’s essential to recognize the symptoms of acute barbiturate poisoning early to initiate treatment promptly.
- Incorrect Treatment: Administering inappropriate treatments, such as narcotics for respiratory depression, can worsen the condition.
- Ignoring Supportive Care: Supportive care, including mechanical ventilation, is crucial in managing severe poisoning cases.
- Failure to Monitor: Continuous monitoring of vital signs (respiration, blood pressure) is vital to prevent complications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What is acute barbiturate poisoning?
A : Acute barbiturate poisoning occurs when someone ingests an overdose of barbiturates, leading to severe central nervous system depression, respiratory issues, and potential death.
Q. How does acute barbiturate poisoning kill the body?
A : The primary cause of death in acute barbiturate poisoning is respiratory depression. As the overdose progresses, the individual may stop breathing, leading to hypoxia and multi-organ failure.
Q. What are the symptoms of acute barbiturate poisoning?
A : Common symptoms include confusion, dizziness, respiratory depression, hypotension, and, in severe cases, coma and death.
Q. How is acute barbiturate poisoning treated?
A : Treatment involves hospitalization, activated charcoal administration (if the poisoning occurred recently), and respiratory support (such as mechanical ventilation) in severe cases.
Conclusion
This poisoning is a serious medical emergency that requires prompt recognition and treatment. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options, medical professionals, MBBS students, and the general public can better manage and prevent the consequences of barbiturate overdoses. Remember, the earlier the intervention, the better the chances of a positive outcome.
Stay informed by subscribing to our newsletter for more health tips, medical insights, and educational resources on toxicology and medical emergencies.
Exam Question–Answer (University Pattern)
Q: Define acute barbiturate poisoning and explain its management.
Answer:
- Definition: Acute barbiturate poisoning occurs due to an overdose of barbiturates, leading to central nervous system depression and respiratory failure.
- Symptoms: Respiratory depression, confusion, hypotension, coma.
- Management:
- Initial assessment: Ensure airway protection, assess vitals.
- Activated Charcoal: Administer if within 1 hour of ingestion.
- Supportive Care: Mechanical ventilation, IV fluids.
- Monitoring: Continuous vital sign monitoring.
Marks Distribution:
- Definition: 2 marks
- Symptoms: 3 marks
- Management: 5 marks